How the hot manure market could tell us about the world
How the hot manure market could tell us about the world



Who would’ve thought that someone is willing to pay a hefty price for turds? Although some might find this to be stomach-churning, it is a reality. According to Bloomberg, manure is selling for USD 40 to 70 per ton, an all-time high level since 2012.
Major reasoning behind this phenomenon could be traced from the ongoing fertiliser crisis, especially from one of its key ingredients: ammonia.
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen (NH3). The high nitrogen component, a key macronutrient for plants, makes ammonia an essential feedstock for all nitrogen-based fertilisers. Alternatively, it can be applied directly to the soil as well.
Based on our study, the dynamic of ammonia market is reflecting today’s problems on multiple fronts, namely: supply chain, agricultural, energy, and geopolitical tension. Its price performance is a perfect example of what could happen when an inelastic demand faces a serious setback in supply.
Perhaps, ammonia could be good long exposure for the ongoing problems in the world. Below is our learning on this matter:
The now deep-pocketed farmers could afford the unprecedented upswings of ammonia price
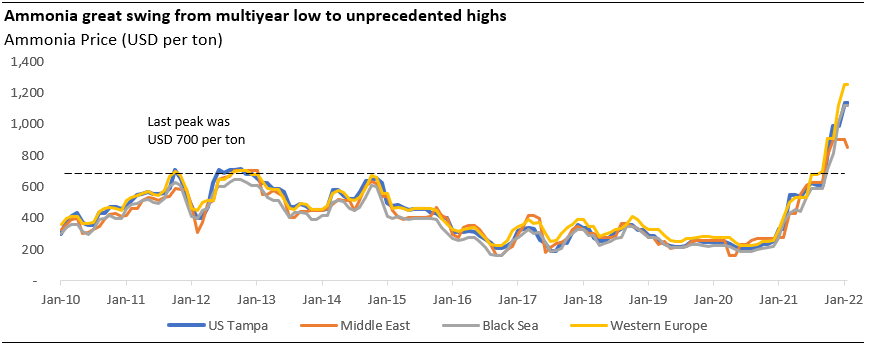
The soaring price of ammonia has a profound impact on the agriculture market as fertilisers typically contribute up to 20% of in-farm cash costs. The ammonia market, however, is also affected by the agriculture market as the chemical is their essential derivative demand – 80% of ammonia use case comes from fertiliser.
Given such a relationship, ammonia price can only elevate that much for a considerable time because there are people who are willing to pay for it. In this case, it is the farmers who account for most of the demand.
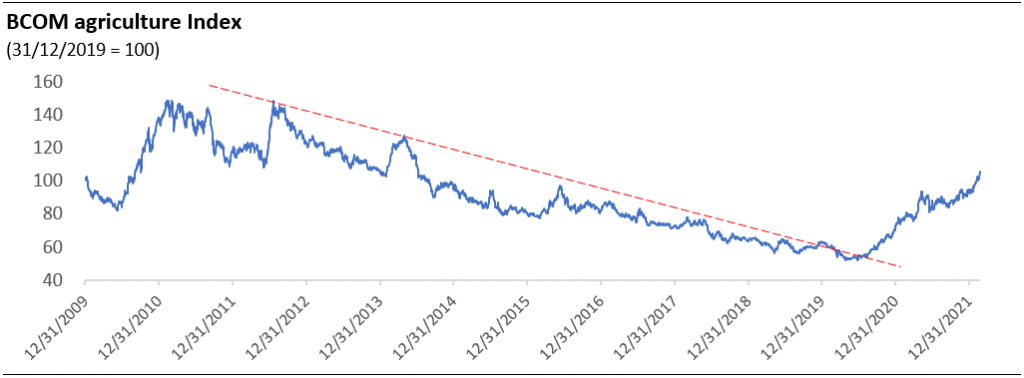
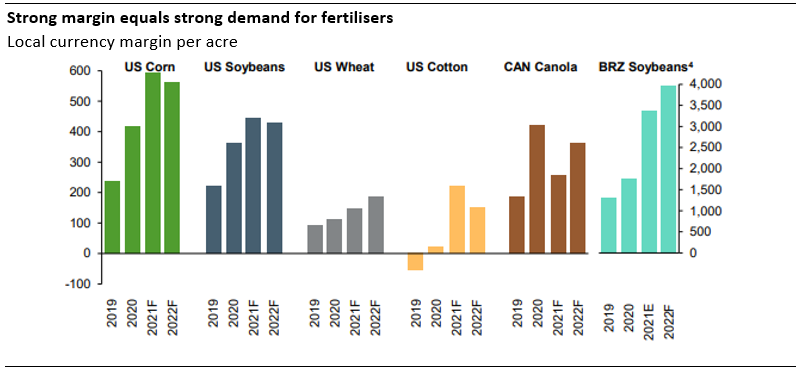
As of 23 February 2022, the Bloomberg agriculture commodity price index was indicated 67% higher than on the end of 2019 level. The favorable agricultural prices certainly have buoyed the fertiliser market as it deepens farmers’ pockets. Nutrien, the world’s largest plant nutrition producer, sees crops producers’ margin to expand by more than two hundred percent for 2021 and 2022 compared to the 2019 level.
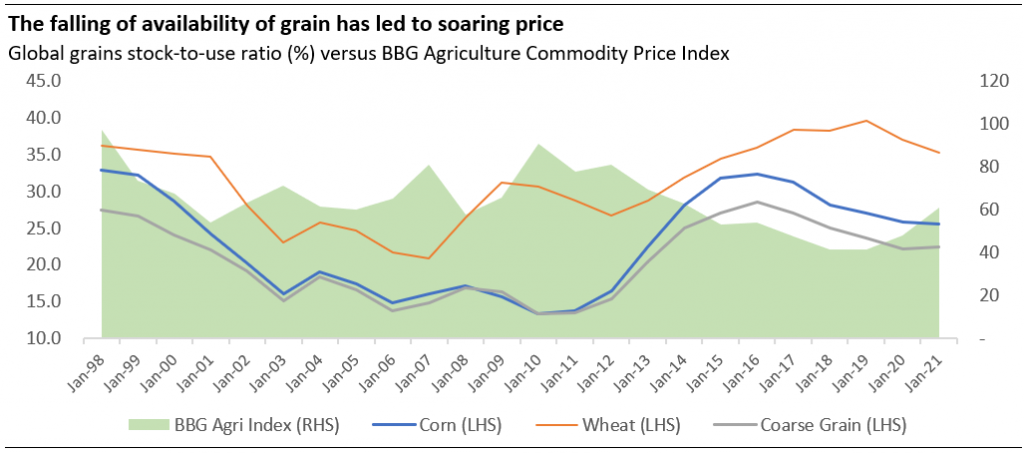
We see the outlook for agricultural commodities to remain bright as the tight market is yet to see relief. Global grains stocks-to-use ratio that indicate the carryover availability to fulfill the full-year demand has been in a free-fall in the last couple of years. The weak prices of 2012-2020 might had disincentivized investments in this space and resulted in a weak production capacity to timely respond to demand.
The combination of economic reopening and stimulus packages during the pandemic is also providing strong support for the demand for agricultural commodities.
Provided by these circumstances, farmers should be well-incentivised to continue applying fertilizers for maintaining or boosting their production. Especially, when they know that in some parts of the world crop yield might be adversely impacted by La Nina.
It is amazing to see this rock-solid demand could afford multiple setbacks on the supply side.
The supply-side problems have dislocated ammonia market by at least 48%
Normally, ammonia plants are built altogether with the downstream fertiliser plants. The statistics of the International Fertilizers Associations (IFA) indicated only 18.4 mn tons of 185.3 mn tons global capacity production in ammonia was traded globally in 2020. Only 10% of global production was intended for trade, causing the merchant ammonia market prone to disruptions.
Based on our estimate, the current ammonia market’s equilibrium faced a dislocation of at least 48% from the 2020 locus due to the following supply-side issues:
- Energy-crisis sent one-third of European ammonia plants to shutdown
Ammonia production process requires hydrogen and involved an energy-intense process. Most of the ammonia plants today are using natural gas as their feedstock for their hydrogen rather than coal or water due to environmental and economical considerations. Natural gas as a feedstock could govern 70-90% of the cash production cost of ammonia, excluding energy cost.
According to Bloomberg Intelligence, currently, about one-third of Europe’s ammonia production plants are being shut down due to the pricey natural gas cost. Such supply gap translates into additional demand to the merchant ammonia market and pinched 30% of the merchant ammonia balance.
The reasoning behind the energy crisis was a combination between structural changes and geopolitical tension:
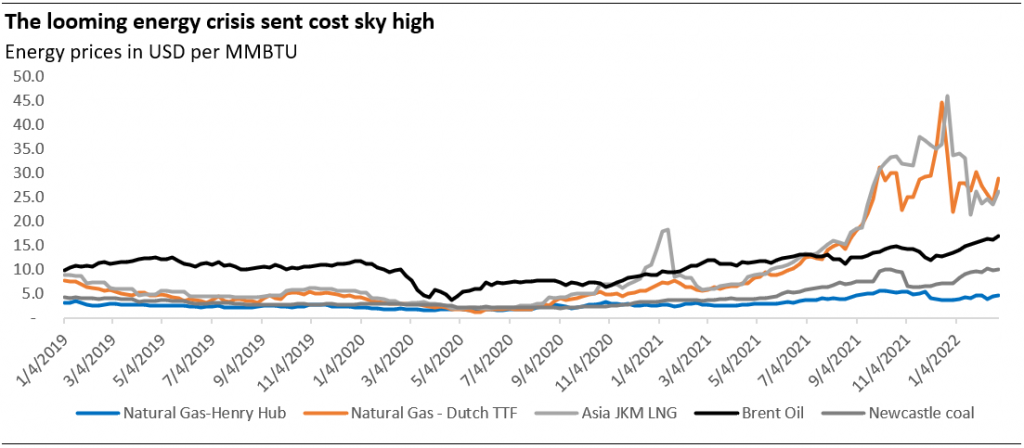
In Q4 2021, we saw the tight energy market take the spotlight and send costs sky-high. The sector underinvestment over the last five years driven by lackluster prices, ESG scrutiny, and global-wide consolidation jolted fossil fuel prices up when it faces a robust demand from economic reopening. We had written some of these matters in our previous blog post in June 2021 (link).
In the case of natural gas, we saw its energy cost per unit has exceeded brent oil in both Europe (Dutch TTF) and Asia (JKM). Indicating the two regions’ competition to secure supply. This was primarily due to the region’s structural shift of adopting natural gas in their path of decarbonization. This structural shift is expected to result in a shortage of LNG in the future according to McKinsey.
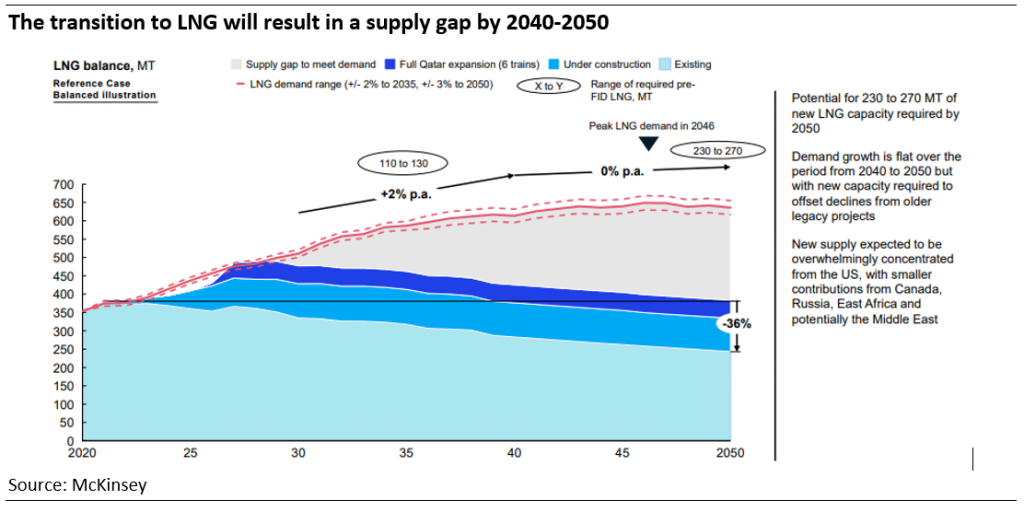
With over 20% gas share in their energy mix, gas demand was amplified because intermittent renewable energy did not work during winter. About 10% to 20% of energy sources had to be switched to ‘dirtier’ hydrocarbon and gas has been the top preference.
This condition is worsened as Russia’s gas flows which account for 40% of Europe’s gas supply are reduced significantly. Russia’s gas flow in December 2021 was 10.3 bcm, about 26% lower than the same period last year.
The recently escalated tension of Russia-Ukraine has resulted in the postponement of the Nordstream II pipeline operation, carving out a significant potential gas supply for the region.
The Dutch TTF’s futures are now trading above USD 20 per MMBTU until mid-2023. This price has priced in the delay of the potential gas supply and implies LNG in Europe won’t be adequate to fill in the gas stock-up in the region for the whole year which starts at a very low base as inventory level is lower than five-year lows.
Warmer winter from La Nina for Europe could help to ease the replenishment of gas production but at this rate, this effect would be rather blunt. With natural gas availability remaining uncertain, we believe that the shutdown of European ammonia producers would take some time and the country will be a dominant buyer in the market.
- Missing fertiliser exports from Russia and China
In attempts to control food prices and security domestically, Russia and China have imposed restrictions on fertilisers export to ensure the availability and affordability for local farmers until 1H22. We estimated this resulted in 18% of missing supply from the merchant ammonia market.
The uncertainty looms whether as the policy would be carried as the initial plan since the tight market in agriculture, potash, nitrogen (ammonia), and phosphate market persist. Not to mention the escalating tension between Ukraine and Russia lingering the uncertainty in the already tight agricultural and energy market.
- Supply chain constraints kept prices high
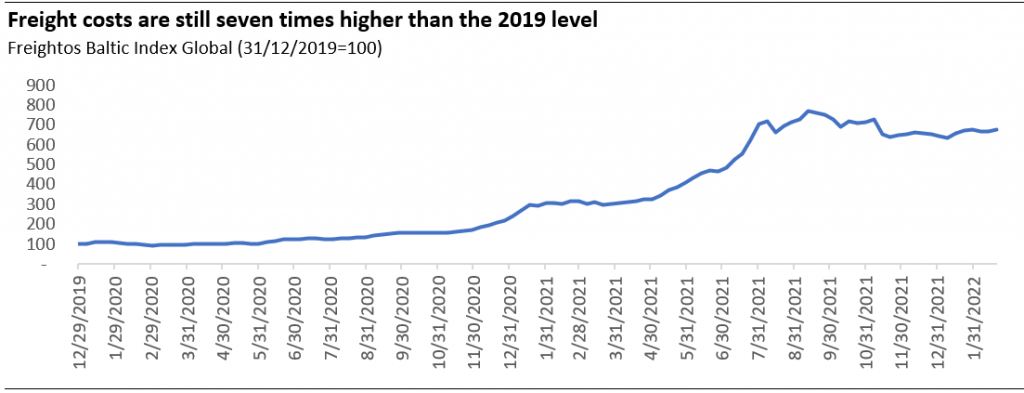
The supply chain problems constraint that was initiated from the COVID-19 pandemic still haunt the economy. The steep freight cost has reportedly caused some producers to switch their inventory policy from just-in-time to just-in-case, stretching up the freight capacity even more.
For Europe and Asia, the steep freight market capped the potential cost savings from importing through LNG freight. Based on the normal calculation, we estimated about half the price of the current LNG price in Europe and Asia is going to the freight.
In addition to supply chain issues, health protocols also delayed the recovery and development of plants. Those factors combined slows down the plant turnaround process from 20 days to 60 days, according to one of our sources in the industry. Another case in point is the development of the Ma’Aden Ammonia-3 plant’s commercialization has been stalled from December 2021 and is expected to be delayed until Q3 2022, a nine-month delay.
Ammonia could be a good long-exposures on today’s world problem
In short, tight agricultural market, energy crisis, geopolitical tension, and supply chain issues are factors that keep ammonia prices high. At the current goldilocks situation, we see European fertiliser companies purchase to set the support price for ammonia as they become the dominant buyer in the market. It still unclear on how long this confluence of problems could be untangled.
So far, the pockets of farmers have been deep enough to pay the high price of ammonia from the tailwind of their commodities. Given the tight relationship of ammonia in the multiple problematic verticals of today’s economy, perhaps ammonia exposure could be a prospective long-exposure towards todays’ world problems?
Admin heyokha
Share

Who would’ve thought that someone is willing to pay a hefty price for turds? Although some might find this to be stomach-churning, it is a reality. According to Bloomberg, manure is selling for USD 40 to 70 per ton, an all-time high level since 2012.
Major reasoning behind this phenomenon could be traced from the ongoing fertiliser crisis, especially from one of its key ingredients: ammonia.
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen (NH3). The high nitrogen component, a key macronutrient for plants, makes ammonia an essential feedstock for all nitrogen-based fertilisers. Alternatively, it can be applied directly to the soil as well.
Based on our study, the dynamic of ammonia market is reflecting today’s problems on multiple fronts, namely: supply chain, agricultural, energy, and geopolitical tension. Its price performance is a perfect example of what could happen when an inelastic demand faces a serious setback in supply.
Perhaps, ammonia could be good long exposure for the ongoing problems in the world. Below is our learning on this matter:
The now deep-pocketed farmers could afford the unprecedented upswings of ammonia price

The soaring price of ammonia has a profound impact on the agriculture market as fertilisers typically contribute up to 20% of in-farm cash costs. The ammonia market, however, is also affected by the agriculture market as the chemical is their essential derivative demand – 80% of ammonia use case comes from fertiliser.
Given such a relationship, ammonia price can only elevate that much for a considerable time because there are people who are willing to pay for it. In this case, it is the farmers who account for most of the demand.
As of 23 February 2022, the Bloomberg agriculture commodity price index was indicated 67% higher than on the end of 2019 level. The favorable agricultural prices certainly have buoyed the fertiliser market as it deepens farmers’ pockets. Nutrien, the world’s largest plant nutrition producer, sees crops producers’ margin to expand by more than two hundred percent for 2021 and 2022 compared to the 2019 level.

We see the outlook for agricultural commodities to remain bright as the tight market is yet to see relief. Global grains stocks-to-use ratio that indicate the carryover availability to fulfill the full-year demand has been in a free-fall in the last couple of years. The weak prices of 2012-2020 might had disincentivized investments in this space and resulted in a weak production capacity to timely respond to demand.
The combination of economic reopening and stimulus packages during the pandemic is also providing strong support for the demand for agricultural commodities.

Provided by these circumstances, farmers should be well-incentivised to continue applying fertilizers for maintaining or boosting their production. Especially, when they know that in some parts of the world crop yield might be adversely impacted by La Nina.
It is amazing to see this rock-solid demand could afford multiple setbacks on the supply side.
The supply-side problems have dislocated ammonia market by at least 48%
Normally, ammonia plants are built altogether with the downstream fertiliser plants. The statistics of the International Fertilizers Associations (IFA) indicated only 18.4 mn tons of 185.3 mn tons global capacity production in ammonia was traded globally in 2020. Only 10% of global production was intended for trade, causing the merchant ammonia market prone to disruptions.
Based on our estimate, the current ammonia market’s equilibrium faced a dislocation of at least 48% from the 2020 locus due to the following supply-side issues:
- Energy-crisis sent one-third of European ammonia plants to shutdown
Ammonia production process requires hydrogen and involved an energy-intense process. Most of the ammonia plants today are using natural gas as their feedstock for their hydrogen rather than coal or water due to environmental and economical considerations. Natural gas as a feedstock could govern 70-90% of the cash production cost of ammonia, excluding energy cost.
According to Bloomberg Intelligence, currently, about one-third of Europe’s ammonia production plants are being shut down due to the pricey natural gas cost. Such supply gap translates into additional demand to the merchant ammonia market and pinched 30% of the merchant ammonia balance.
The reasoning behind the energy crisis was a combination between structural changes and geopolitical tension:

In Q4 2021, we saw the tight energy market take the spotlight and send costs sky-high. The sector underinvestment over the last five years driven by lackluster prices, ESG scrutiny, and global-wide consolidation jolted fossil fuel prices up when it faces a robust demand from economic reopening. We had written some of these matters in our previous blog post in June 2021 (link).
In the case of natural gas, we saw its energy cost per unit has exceeded brent oil in both Europe (Dutch TTF) and Asia (JKM). Indicating the two regions’ competition to secure supply. This was primarily due to the region’s structural shift of adopting natural gas in their path of decarbonization. This structural shift is expected to result in a shortage of LNG in the future according to McKinsey.

With over 20% gas share in their energy mix, gas demand was amplified because intermittent renewable energy did not work during winter. About 10% to 20% of energy sources had to be switched to ‘dirtier’ hydrocarbon and gas has been the top preference.
This condition is worsened as Russia’s gas flows which account for 40% of Europe’s gas supply are reduced significantly. Russia’s gas flow in December 2021 was 10.3 bcm, about 26% lower than the same period last year.
The recently escalated tension of Russia-Ukraine has resulted in the postponement of the Nordstream II pipeline operation, carving out a significant potential gas supply for the region.
The Dutch TTF’s futures are now trading above USD 20 per MMBTU until mid-2023. This price has priced in the delay of the potential gas supply and implies LNG in Europe won’t be adequate to fill in the gas stock-up in the region for the whole year which starts at a very low base as inventory level is lower than five-year lows.
Warmer winter from La Nina for Europe could help to ease the replenishment of gas production but at this rate, this effect would be rather blunt. With natural gas availability remaining uncertain, we believe that the shutdown of European ammonia producers would take some time and the country will be a dominant buyer in the market.
- Missing fertiliser exports from Russia and China
In attempts to control food prices and security domestically, Russia and China have imposed restrictions on fertilisers export to ensure the availability and affordability for local farmers until 1H22. We estimated this resulted in 18% of missing supply from the merchant ammonia market.
The uncertainty looms whether as the policy would be carried as the initial plan since the tight market in agriculture, potash, nitrogen (ammonia), and phosphate market persist. Not to mention the escalating tension between Ukraine and Russia lingering the uncertainty in the already tight agricultural and energy market.
- Supply chain constraints kept prices high

The supply chain problems constraint that was initiated from the COVID-19 pandemic still haunt the economy. The steep freight cost has reportedly caused some producers to switch their inventory policy from just-in-time to just-in-case, stretching up the freight capacity even more.
For Europe and Asia, the steep freight market capped the potential cost savings from importing through LNG freight. Based on the normal calculation, we estimated about half the price of the current LNG price in Europe and Asia is going to the freight.
In addition to supply chain issues, health protocols also delayed the recovery and development of plants. Those factors combined slows down the plant turnaround process from 20 days to 60 days, according to one of our sources in the industry. Another case in point is the development of the Ma’Aden Ammonia-3 plant’s commercialization has been stalled from December 2021 and is expected to be delayed until Q3 2022, a nine-month delay.
Ammonia could be a good long-exposures on today’s world problem
In short, tight agricultural market, energy crisis, geopolitical tension, and supply chain issues are factors that keep ammonia prices high. At the current goldilocks situation, we see European fertiliser companies purchase to set the support price for ammonia as they become the dominant buyer in the market. It still unclear on how long this confluence of problems could be untangled.
So far, the pockets of farmers have been deep enough to pay the high price of ammonia from the tailwind of their commodities. Given the tight relationship of ammonia in the multiple problematic verticals of today’s economy, perhaps ammonia exposure could be a prospective long-exposure towards todays’ world problems?
Admin heyokha
Share