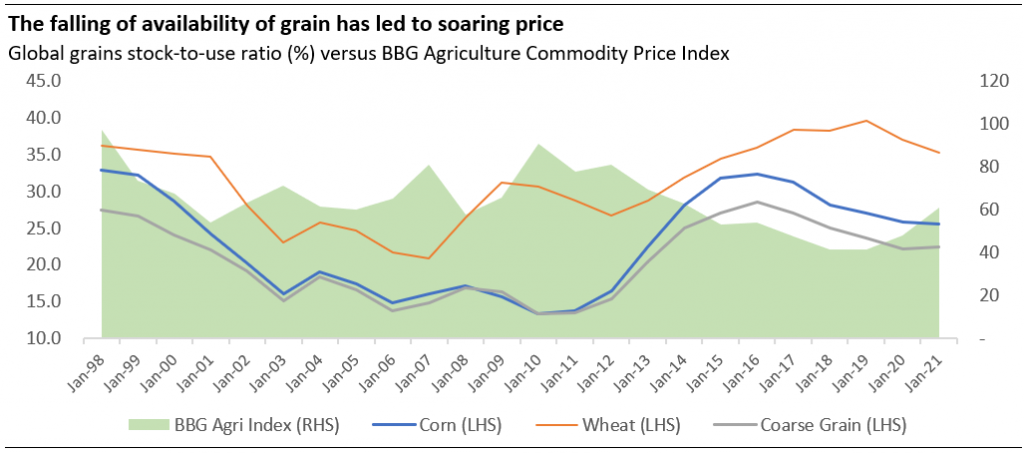
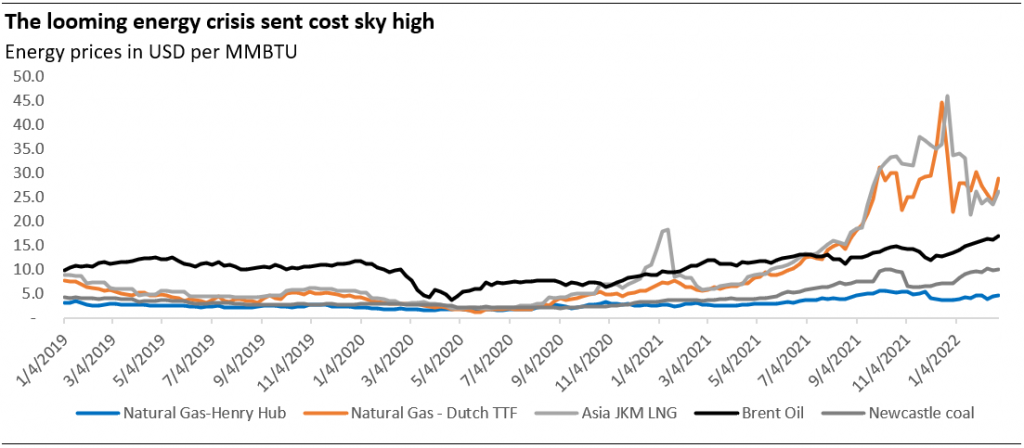
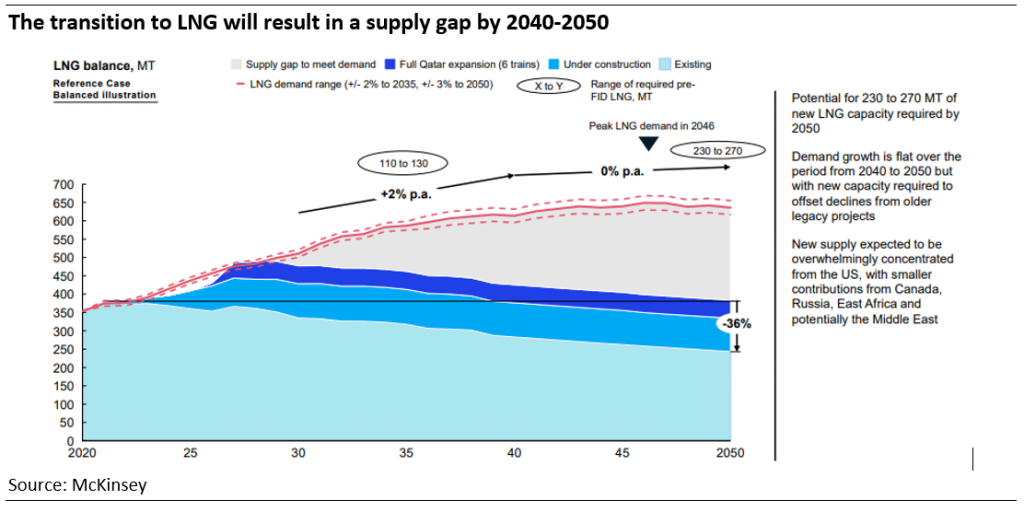
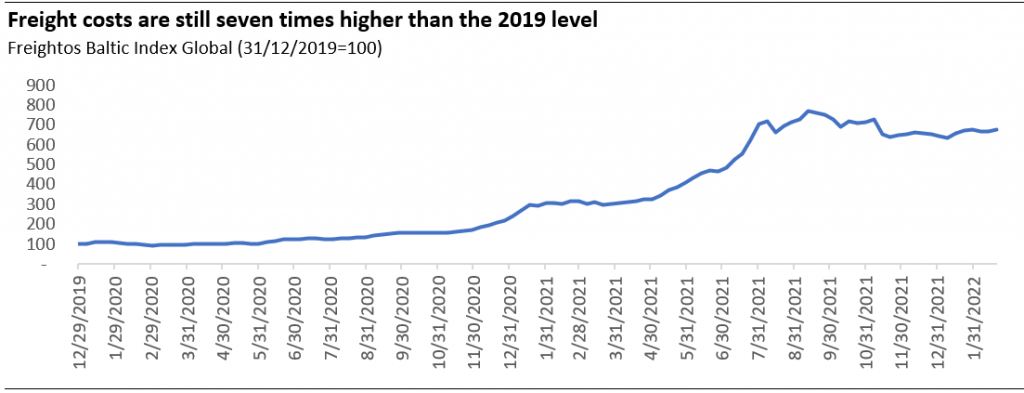
One of the wake-up calls during the still on-going Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is how the market witnessed the US and EU utilising the powerful tool of economic warfare by barring Russia from accessing its billions of foreign reserves (except using the reserves for energy payments.) As a result of this sanction imposed against Russia, calls have been raised for the need for alternative holdings.
Being the top holder of foreign currency reserves with $3.22 trillion as of January 2022, with over two and a half times more than the second-largest reserve holder, as well as a friend of Russia, it will come as no surprise if China decides to unshackle itself from the dollar-dominated system in order to reduce their reliance on US dollar.
De-dollarisation is not only limited to China, it is reported by The Wall Street Journal that “Saudi Arabia is in active talks with Beijing to price some of its oil sales to China in yuan,” a move that could further erode US dollar reserve currency’s status. And one should also notice that the Middle East, led by Bahrain and the UAE, is setting up some of the world’s largest crypto exchanges spearheaded by FTX (who have decided to leave HK) and Binance.
No matter how the war of tragedy unfolds, it has signalled to some countries the need to reduce their reliance on SWIFT – the global messaging system between banks to ensure financial security. In fact, Russia’s central bank has developed its own alternative to Swift called the System for Transfer of Financial Messages since 2014, when the US government threatened to disconnect Russia from SWIFT. But it is nowhere near as big as the former.
Having said that, with cryptocurrencies becoming more mainstream, the long race to catch up may not be necessarily if blockchain technology is here to provide a powerful alternative to the legacy global messaging system in the coming years.
Blockchain as a backbone for global finance may still be remote, but we have witnessed how crypto has marked its place in the war.
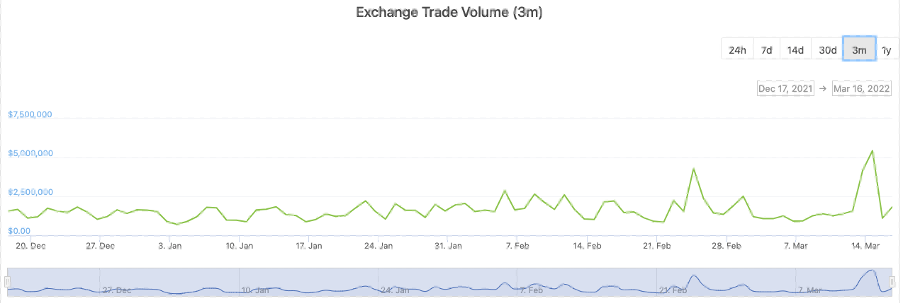
With Ukraine’s central bank limiting its citizens from withdrawing foreign currency, some Ukrainians have turned to crypto as an alternative. Crypto trading volume on Ukraine’s Kuna Exchange had surged 200% in the last week of February, reaching its highest level since May 2021. The country has also raised over $50 million in crypto donation, as indicated on its official donation website.
On the other hand, crypto could also be used as an escape route for Russia.
The fact that cryptocurrencies cannot be frozen (let’s rule out centralised crypto wallets for now), has made these tokens an extremely important tool. The Bank of Russia has been developing the digital rubles and has already started the pilot stage of its CBDC before the war began. The call to ban selective Russian banks from the international payment system may have motivated the Russian government to speed up the progress.
Despite no clear evidence of Russians rushing to crypto for a safe haven as information is limited about the country lately, we are witnessing regulators around the world ramping up their efforts in the cryptocurrencies space. Perhaps one of the motives behind this could also be the attempt to close any potential loopholes in the sanctions. While we hope that the conflict can be quickly resolved, if sanctions have become a norm rather than exception, we should all think about what self-sovereignty means to our wealth.
The global CBDC race
On 9th March 2022, US President Joe Biden signed an executive order on digital assets, including cryptocurrencies. While the order did not specifically launch any new policies, but only guidelines for the upcoming steps, it marked the first official strategy on digital assets set forth by the US government and has given the crypto industry the regulatory clarity that has been long sought after.
The executive order outlined a number of policy priorities and risks related to the implications brought by digital assets, first and foremost is customer and investor protection, followed by financial stability and systematic risk, national security, energy demand and climate change, etc. The executive order contains a well balance of discussion on both the opportunities and risks.
No commitments were made to a US Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), but the executive order specifically called for the “urgency” for the Fed to double down their research on CBDC. We see this as a pursuit to put the US on a level playing field with China who has launched its CBDC pilot last month.
Just days after the executive order was signed, the European Parliament voted to advance a draft of the Markets in Crypto Assets bill, or MiCA, which is a regulatory framework for crypto assets that has been in development since 2018. A lot of similarities could be found between the executive order and the MiCA.
The uniform framework for the EU’s 27 member states also covers rules on supervision, consumer protection and environmental sustainability of crypto assets. An earlier addition to the bill that aimed to limit the use of cryptocurrencies powered by the energy-intensive consensus mechanism known as proof-of-work, which essentially means banning crypto such as Bitcoin and Ethereum in the EU, was voted down by the committee.
Alternatively, the committee voted in favour of a proposal to include crypto-assets mining in EU taxonomy for sustainable activities by 2025 to reduce carbon footprint. The EU has begun its digital euro project since July 2021 and the current investigation phase is expected to take two years. One thing to note is that the MiCA will not be applied to CBDCs.
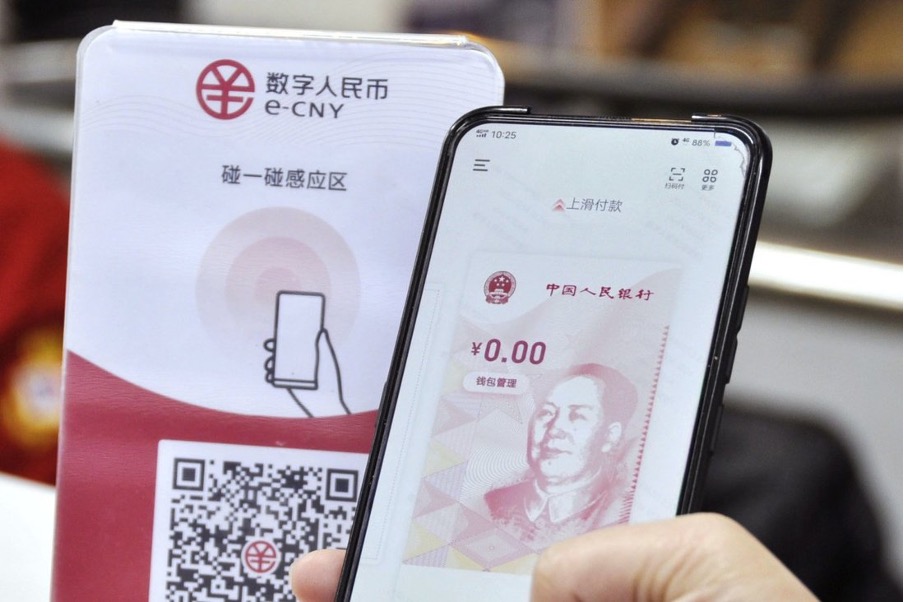
While the US and the EU have just started with the entrée, China is enjoying the dessert. After eight years in development, China has debuted the digital yuan, its version of CBDC, during the Beijing Winter Olympic Games last month, subsequent to its trial launched in late 2019. According to the data released by the Chinese government, the digital yuan was accepted by more than 8 million merchants and over RMB 87 billion in transaction value was reached as of the end of last year. The next step for China would be to follow its plan outlined in the 14th Five-Year Plan, further expanding the development of the digital currency alongside its digital economy.
Image Source: Kyodo
Last but not least, the Hong Kong Secretary for Financial Services and the Treasury released a letter through his blog yesterday, announcing the government’s latest development in regulating the virtual asset industry. Although there is no explicit timeline for the next steps, the letter highlighted the government’s consideration to introduce a new licensing regime for virtual assets service providers in accordance with the requirement imposed by the Financial Action Task Force which requires all virtual assets exchanges to apply for a license from the Securities and Futures Commission.
If 2021 was marked as the year that made crypto and NFT broke out of their niche, 2022 would be the year of crypto regulation. And with over 80 countries currently exploring a CBDC, we think digital currencies are here to stay and disrupt the traditional financial system. These are still early days for CBDCs and we do not know how fast and far they will go.
But we are excited.
Reference:
https://data.imf.org/regular.aspx?key=61280813
https://donate.thedigital.gov.ua/
http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-02/23/content_5675094.htm
https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/cbdctracker/
Admin heyokha
Share
One of the wake-up calls during the still on-going Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is how the market witnessed the US and EU utilising the powerful tool of economic warfare by barring Russia from accessing its billions of foreign reserves (except using the reserves for energy payments.) As a result of this sanction imposed against Russia, calls have been raised for the need for alternative holdings.
Being the top holder of foreign currency reserves with $3.22 trillion as of January 2022, with over two and a half times more than the second-largest reserve holder, as well as a friend of Russia, it will come as no surprise if China decides to unshackle itself from the dollar-dominated system in order to reduce their reliance on US dollar.
De-dollarisation is not only limited to China, it is reported by The Wall Street Journal that “Saudi Arabia is in active talks with Beijing to price some of its oil sales to China in yuan,” a move that could further erode US dollar reserve currency’s status. And one should also notice that the Middle East, led by Bahrain and the UAE, is setting up some of the world’s largest crypto exchanges spearheaded by FTX (who have decided to leave HK) and Binance.
No matter how the war of tragedy unfolds, it has signalled to some countries the need to reduce their reliance on SWIFT – the global messaging system between banks to ensure financial security. In fact, Russia’s central bank has developed its own alternative to Swift called the System for Transfer of Financial Messages since 2014, when the US government threatened to disconnect Russia from SWIFT. But it is nowhere near as big as the former.
Having said that, with cryptocurrencies becoming more mainstream, the long race to catch up may not be necessarily if blockchain technology is here to provide a powerful alternative to the legacy global messaging system in the coming years.
Blockchain as a backbone for global finance may still be remote, but we have witnessed how crypto has marked its place in the war.
With Ukraine’s central bank limiting its citizens from withdrawing foreign currency, some Ukrainians have turned to crypto as an alternative. Crypto trading volume on Ukraine’s Kuna Exchange had surged 200% in the last week of February, reaching its highest level since May 2021. The country has also raised over $50 million in crypto donation, as indicated on its official donation website.
On the other hand, crypto could also be used as an escape route for Russia.
The fact that cryptocurrencies cannot be frozen (let’s rule out centralised crypto wallets for now), has made these tokens an extremely important tool. The Bank of Russia has been developing the digital rubles and has already started the pilot stage of its CBDC before the war began. The call to ban selective Russian banks from the international payment system may have motivated the Russian government to speed up the progress.
Despite no clear evidence of Russians rushing to crypto for a safe haven as information is limited about the country lately, we are witnessing regulators around the world ramping up their efforts in the cryptocurrencies space. Perhaps one of the motives behind this could also be the attempt to close any potential loopholes in the sanctions. While we hope that the conflict can be quickly resolved, if sanctions have become a norm rather than exception, we should all think about what self-sovereignty means to our wealth.
The global CBDC race
On 9th March 2022, US President Joe Biden signed an executive order on digital assets, including cryptocurrencies. While the order did not specifically launch any new policies, but only guidelines for the upcoming steps, it marked the first official strategy on digital assets set forth by the US government and has given the crypto industry the regulatory clarity that has been long sought after.
The executive order outlined a number of policy priorities and risks related to the implications brought by digital assets, first and foremost is customer and investor protection, followed by financial stability and systematic risk, national security, energy demand and climate change, etc. The executive order contains a well balance of discussion on both the opportunities and risks.
No commitments were made to a US Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), but the executive order specifically called for the “urgency” for the Fed to double down their research on CBDC. We see this as a pursuit to put the US on a level playing field with China who has launched its CBDC pilot last month.
Just days after the executive order was signed, the European Parliament voted to advance a draft of the Markets in Crypto Assets bill, or MiCA, which is a regulatory framework for crypto assets that has been in development since 2018. A lot of similarities could be found between the executive order and the MiCA.
The uniform framework for the EU’s 27 member states also covers rules on supervision, consumer protection and environmental sustainability of crypto assets. An earlier addition to the bill that aimed to limit the use of cryptocurrencies powered by the energy-intensive consensus mechanism known as proof-of-work, which essentially means banning crypto such as Bitcoin and Ethereum in the EU, was voted down by the committee.
Alternatively, the committee voted in favour of a proposal to include crypto-assets mining in EU taxonomy for sustainable activities by 2025 to reduce carbon footprint. The EU has begun its digital euro project since July 2021 and the current investigation phase is expected to take two years. One thing to note is that the MiCA will not be applied to CBDCs.
While the US and the EU have just started with the entrée, China is enjoying the dessert. After eight years in development, China has debuted the digital yuan, its version of CBDC, during the Beijing Winter Olympic Games last month, subsequent to its trial launched in late 2019. According to the data released by the Chinese government, the digital yuan was accepted by more than 8 million merchants and over RMB 87 billion in transaction value was reached as of the end of last year. The next step for China would be to follow its plan outlined in the 14th Five-Year Plan, further expanding the development of the digital currency alongside its digital economy.
Image Source: Kyodo
Last but not least, the Hong Kong Secretary for Financial Services and the Treasury released a letter through his blog yesterday, announcing the government’s latest development in regulating the virtual asset industry. Although there is no explicit timeline for the next steps, the letter highlighted the government’s consideration to introduce a new licensing regime for virtual assets service providers in accordance with the requirement imposed by the Financial Action Task Force which requires all virtual assets exchanges to apply for a license from the Securities and Futures Commission.
If 2021 was marked as the year that made crypto and NFT broke out of their niche, 2022 would be the year of crypto regulation. And with over 80 countries currently exploring a CBDC, we think digital currencies are here to stay and disrupt the traditional financial system. These are still early days for CBDCs and we do not know how fast and far they will go.
But we are excited.
Reference:
https://data.imf.org/regular.aspx?key=61280813
https://donate.thedigital.gov.ua/
http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-02/23/content_5675094.htm
https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/cbdctracker/
Admin heyokha
Share